Abstract
Introduction: Salivary gland disorders can arise from
infection, inflammation, cystic changes, degenerative
process and neoplastic etiologies. Most common
conditions of salivary gland disease result from acute
infection and inflammation. These swellings can
usually be diagnosed clinically .Reports of salivary
gland tumours are also on the rise, with one study
revealing the incidence to be 6% of all head and
neck tumors.
Materials and methods: Retrospective
analysis of salivary gland swellings, diagnosed by
fine needle aspiration cytology from Kartik 2072 to
Chaitra 2074, was done.
Result: The most common
age group with manifestation of salivary gland
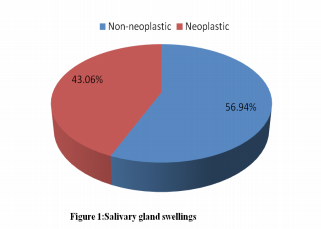
pathology was 11-20 years (19.4%). Non neoplastic
swellings comprised 56% of the cases, while the
rest comprised of neoplastic swellings. Conclusion:
Chronic infection and pleomorphic adenoma were
the most common diseases involving salivary glands
are, among nonneoplastic and neoplastic group
respectively.
Keywords: salivary gland, malignancy,
benign tumours, sialdenitis
References
Pathology and genetics of head and neck tumours.
Lyon:IARC/Press; 2005.
2. Fernandes H,D’souza CR, Khosla C, George
L, Katte NH. Role of FNAC in the preoperative
diagnosis of salivary gland lesions. J Clin Diagn
Res. 2014 Sep;8(9).
3. Sandhu VK, Sharma U, Singh N, Puri A.
Cytological spectrum of salivary gland lesions and
their correlation with epidemiological parameters.
JOMFP. 2017 Aug;21(2): 203-10.
4. Wilson KF, Meier JD, Ward PD. Salivary gland
disorders. Am Fam Physician. 2014 Jun;89(11):882-
8.
5. Porter SR. Non-neoplastic salivary gland
diseases. In: Gleeson M, Browning G, Burton MJ,
Clarke R, Hibbert J, Jones N et al. Scott-Brown’s
Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery. 7 nd
ed. London: Hodder Arnold; 2008. p 1898-1916.
6. Delli K, Spijkervet FK, Vissink A. Salivary
gland diseases:infections,sialolithiasis and
mucoceles. Monogr Oral Sci. 2014 May;24:135-
48.
7. Pandey A, Pandey M, Pandey VP, Ravindran
V. Oral manifestations of autoimmune connective
tissue diseases. Indian J Rheumatol 2018;13:264-
72.
8. Omhare A, Singh SK, Nigam JS, Sharma A.
Cytohistopathological Study of Salivary Gland
Lesions in Bundelkhand Region, Uttar Pradesh,
India. Pathology Research International. 2014
Aug;5.
9. Jones AV, Craig GT, Speight PM, Franklin CD.
The range and demographics of salivary gland
tumours diagnosed in a UK population. Oral
oncology. 2008 Apr; 44(4): 407-17.
10.Subhashraj K. Salivary gland tumors:a single
institution experience in India. British Journal
of oral and maxillofacial surgery. 2008 Dec;
46(8):635-8