Abstract
Introduction: The aim of the study was to observe the
success rate of extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL)
in the management of upper urinary tract stones.
Materials and Methods: This retroprospective study was
conducted in Pokhara Kidney stone Centre, Pokhara, Kaski,
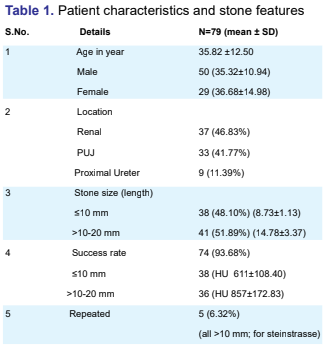
Nepal from January 2017 to January 2018. Seventy nine
patients were selected in this study with upper urinary tract
stone, size less than 20mm.
Results: Seve nty four (93.67%) patients were successfully
treated in initial use of shock wave and 5 (6.32%) patients
required repetition.
Conclusion: Overall satisfactory success rate was observed
using ESWL for the upper urinary tract stone. Careful selection
of patient, stone size and Hounsfield unit (HU) is advisable.
References
Dec;2:1265–8.
2. Vilches R.M, Aliaga A, Reyes D, Sepulveda F, Mercado A, Moya F, et al. Comparison between retrograde intrarenal surgery and
extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy in the treatment of lower pole kidney stones up to 15 mm. Prospective, randomized study.
Actas Urológicas Españolas. 2014 Nov;39(4): 236-242
3. Turk C, Petrik A, Sarica K, Seitz C, Skolarikos A, Straub M, et al. EAU Guidelines on Intervention Treatment for Urolithiasis.
European Association of Urology. 2015 july;041:18-20.
4. Madaan S, Joyce AD. Limitations of extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy. Curr Opin Urol. 2007 April;17:109–13.
5. Gerber R, Studer UE, Danuser H. Is newer always better? A comparative study of 3 lithotriptor generations. J Urol. 2005
Jun;173:2013–6.
6. Wu H, Wang J, LU J, Wang Y, Niu Z. Treatment of renal stone ≥20 mm with extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy. Urol Int. 2016
Jan;96:99-105
7. Nielsen TK, Jensen JB. Efficacy of commercialised extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy service: a review of 589 renal stones.
BMC Urology. 2017 Jul;17(1):59.
8. Shafi H, Moazzami B, Pourghasem M, Kasaeian A. An overview of treatment options for urinary stones. Caspian J Internal Med.
2016 Oct;7(1):1-6.
9. Klein J, Netsch C, Sievert KD, Miernik A, Westphal J, Leyh H, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy. Urologe A. 2018
Apr;57(4):463-473.
10. Moody JA, Evans AP, Lingeman JE. Extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy. In: Weiss RM, George NJR, O’Reilly PH, editors.
Comprehensive urology. 1st ed. Mosby International Limited; 2001;pp 623–36.
11. Hamal BK, Bhandari BB, Thapa N. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy in Management of Urolithiasis. Journal of Patan
Academy of Health Sciences. 2014 Jun;1(1):4-7
12. Shrestha B, Baidya JL. Outcome of extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy at B and B Hospital.J Nepal Med Assoc. 2010 Jan-
Mar;49(177):38-42.
13. Ghimire P, Yogi N, Acharya GB. Outcome of Extracorporeal Shock wave Lithotripsy in Western region of Nepal. Nepal Journal of
Medical Sciences. 2012 Jan-June;1(1):3-6.
14. Joshi HN, Karmacharya RM, Shrestha R, Shrestha B, de Jong IJ, Shrestha RK. Outcomes of Extra Corporeal Shock Wave
Lithotripsy (ESWL) in Renal and Ureteral Calculi. Kathmandu Univ Med J. 2014 Jan-March;45(1):51-54.
15. Sharma UK, KC Nagendra. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy for urolithiasis; a single center study. Journal of Institute of
Medicine. 2013 August;35(2):77-82