Abstract
Background: Treatment of distal tibial metaphyseal fractures is
often challenging and no single technique has been unanimously
advocated. Open reduction and internal fixation with plates and
screws allows better restoration of anatomical alignment but with
more soft tissue complication. Simultaneous fixation of the fibula
is not universally carried out. This study aims at evaluation of the
outcome of plating technique and the effect of fixation of fibula fracture
in treatment of distal tibial metaphyseal fractures.
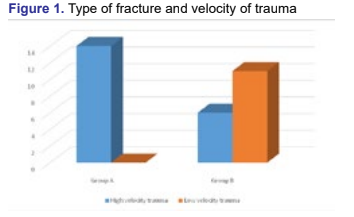
Material and methods: Thirty-one cases (14 cases in Group A
with concomitant distal fibula fracture and 17 cases in Group B without
distal fibula fracture) were analyzed retrospectively for the mean
duration of full weight bearing, mean union time and complications,
and compared.
Results: The mean time for full weight bearing and radiological
union in our study was 14.2 weeks (15.9 in Group A and 13.1 in Group
B) and 23.8 weeks (26.6 in Group A and 21.5 in Group B) respectively.
16.1% of cases had post-operative complications including one case
of deep infection and malalignment of 6 degree varus (following
delayed union) was seen in one case of Group A. Range of motion
(ROM) at ankle was not problem in any of the cases except the one
delayed union which had 5 degrees of dorsiflexion and 15 degrees of
plantiflexion.
Conclusion: Open reduction and internal fixation with plate and
screws in distal tibial metaphyseal fracture is more economic means
of treatment modality with comparable incidence of post-union
malalignment and union time,though more soft tissue complications
compared to other modalities. Fixation of fibula fracture aids in
reducing the incidence of malalignment.
References
minimally invasive plating. Archives of orthopaedic and trauma surgery. 2005;125(2):87-94.
2. Vallier HA, Cureton BA, Patterson BM. Randomized, prospective comparison of plate versus intramedullary nail fixation for
distal tibia shaft fractures. Journal of orthopaedic trauma. 2011;25(12):736-41.
3. Manninen M, Lindahl J, Kankare J, Hirvensalo E. Lateral approach for fixation of the fractures of the distal tibia. Outcome of 20
patients. Archives of orthopaedic and trauma surgery. 2007;127(5):349-53.
4. Digby JM, Holloway GM, Webb JK. A study of function after tibial cast bracing. Injury. 1983;14(5):432-9.
5. Sarmiento A, Sharpe FE, Ebramzadeh E, Normand P, Shankwiler J. Factors influencing the outcome of closed tibial fractures
treated with functional bracing. Clinical orthopaedics and related research. 1995(315):8-24.
6. Lang GJ, Cohen BE, Bosse MJ, Kellam JF. Proximal third tibial shaft fractures. Should they be nailed? Clinical orthopaedics and
related research. 1995(315):64-74.
7. Im G-I, Tae S-K. Distal metaphyseal fractures of tibia: a prospective randomized trial of closed reduction and intramedullary nail
versus open reduction and plate and screws fixation. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery. 2005;59(5):1219-23.
8. Aksekili M, Celik I, Arslan AK, Kalkan T, Uğurlu M. The results of minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) in
distal and diaphyseal tibial fractures. Acta orthopaedica et traumatologica turcica. 2012;46(3):161-7.
9. Francois J, Vandeputte G, Verheyden F, Nelen G. Percutaneous plate fixation of fractures of the distal tibia. Acta orthopaedica
belgica. 2004;70(2):148-54.
10. Kaspar K, Schell H, Seebeck P, Thompson MS, Schütz M, Haas N, et al. Angle stable locking reduces interfragmentary
movements and promotes healing after unreamed nailing: Study of a displaced osteotomy model in sheep tibiae. JBJS.
2005;87(9):2028-37.
11. Augat P, Burger J, Schorlemmer S, Henke T, Peraus M, Claes L. Shear movement at the fracture site delays healing in a
diaphyseal fracture model. Journal of orthopaedic research. 2003;21(6):1011-7.
12. Park S-H, O'connor K, McKellop H, Sarmiento A. The influence of active shear or compressive motion on fracture-healing.
JBJS. 1998;80(6):868-78.
13. Joslin C, Eastaugh-Waring S, Hardy J, Cunningham JL. Weight bearing after tibial fracture as a guide to healing. Clinical
Biomechanics. 2008;23(3):329-33.
14. Hazarika S, Chakravarthy J, Cooper J. Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia—results in
20 patients. Injury. 2006;37(9):877-87.
15. Redfern D, Syed S, Davies S. Fractures of the distal tibia: minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Injury. 2004;35(6):615-20.
16. Cheng W, Li Y, Manyi W. Comparison study of two surgical options for distal tibia fracture—minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis
vs. open reduction and internal fixation. International orthopaedics. 2011;35(5):737-42.
17. Bahari S, Lenehan B, Khan H, McElwain JP. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures. Acta
Orthopædica Belgica. 2007;73(5):635.
18. Yang S-W, Tzeng H-M, Chou Y-J, Teng H-P, Liu H-H, Wong C-Y. Treatment of distal tibial metaphyseal fractures: plating versus
shortened intramedullary nailing. Injury. 2006;37(6):531-5.
19. Höntzsch D, Schaser K-D, Hofmann GO, Pohlemann T, Hem ES, Rothenbach E, et al. Evaluation of the effectiveness of the
angular stable locking system in patients with distal tibial fractures treated with intramedullary nailing: a multicenter randomized
controlled trial. JBJS. 2014;96(22):1889-97.
20. Nork SE, Schwartz AK, Agel J, Holt SK, Schrick JL, Winquist RA. Intramedullary nailing of distal metaphyseal tibial
fractures. JBJS. 2005;87(6):1213-21.
21. Zelle BA, Bhandari M, Espiritu M, Koval KJ, Zlowodzki M, Group E-BOTW. Treatment of distal tibia fractures
without articular involvement: a systematic review of 1125 fractures. Journal of orthopaedic trauma.
2006;20(1):76-9.