Abstract
Background: Monitored anaesthesia care is a specific
anaesthesia service for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures
performed under local anaesthesia along with sedation and
analgesia titrated to a level with the provision to convert
into general anaesthesia when required. We conducted a
retrospective study to determine patient satisfaction in middle
ear surgery under monitored anaesthesia care.
Materials and Methods: The number of patients undergoing
middle ear surgery under monitored anaesthesia care, over
a period of one year were included. They received sedation
with midazolam 0.02 mg/kg and fentanyl 1 mcg/kg along
with local anaesthetic infiltration. Patient’s satisfaction was
measured using a five point Likert scale. Intraoperative pain,
nausea, vomiting and other discomforts were inquired.
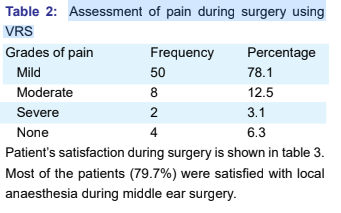
Results: The total number of patients was 64. Fifty-one
patients (79.7%) were satisfied, 10 were neutral (15.6%)
and 3 patients (4.7%) were dissatisfied with the technique.
Earache (4.7%), followed by dizziness (3.1%) and bodyache
(3.1%) were the most common cause of discomfort. Nausea
occurred in 6 patients (9.4%) and vomiting in 5 patients
(7.8%).
Conclusion: Middle ear surgeries can be performed under
monitored anaesthesia care with good patient satisfaction.
References
2. Ghisi D, Fanelli A, Tosi M, Nuzzi M, Fanelli G. Monitored anaesthesia care. Minerva Anestesiol. 2005;71:533–8.
3. ASA. Distinguishing Monitored Anaesthesia Care (“ MAC ”) from Moderate Sedation/ Analgesia (Con scious Sedation). Available
from http://www.asahq.org/~/media/Sites/ASAHQ/Files/Public/Resources/ standards-guidelines/distinguishing-monitored-
anesthesia-care-from-moderate-sedation-analgesia.pdf.
4. Abdellatif AA, Elkabarity RH, Hamdy TAE. Dexmedetomedine vs midazolam sedation in middle ear surgery under local
anaesthesia: Effect on surgical field and patient satisfaction. Egypt J Anaesth [Internet]. 2012;28(2):117–23.
5. Lee JJ, Lee JH. Middle-ear surgery under sedation: Comparison of midazolam alone or midazolam with remifentanil. J Laryngol
Otol. 2011;125(6):561–6.
6. Sarmento KMDA, Tomita S. Retroauricular tympanoplasty and tympanomastoidectomy under local anaesthesia and sedation.
Acta Otolaryngol. 2009;129(7):726–8.
7. Parajuli R, Shrivastav RP, Bhattarai H. Patients ’ Satisfaction in Modified Radical Mastoidectomy Done Under Local
Anaesthesia for Squamous Type of Chronic Otitis Media. Glob J Oto 2017;3(5): 555-624.
8. Fagan J. Open Access Atlas of Otolaryngology , Head & Neck Operative Surgery. Atlas Otolaryngol, Head Neck Oper Surg
[Internet]. 2008;(Figure 1):1–12. Available from: www.entdev.uct.ac.za
9. Parikh D, Kolli S, Karnik H, Lele S, Tendolkar B. A prospective randomized double-blind study comparing dexmedetomidine
vs. combination of midazolam-fentanyl for tympanoplasty surgery under monitored anaesthesia care. J Anaesthesiol Clin Phar
macol [Internet]. 2013;29(2):173.
10. Edussuriya B, Goonasekera C, Rajapakse M. Middle ear surgery under local anaesthesia and sedation. Ceylon Med [Internet].
1997;(July 1997). Available from:https://www.researchgate.net/profile/ Chulananda_Goonasekera/publication/13963651_Mid
dle_ear_surgery_under_local_anaesthesia_and_ sedation/links/565dc20208aeafc2aac889c8.pdf
11. Candiotti KA, Bergese SD, Bokesch PM, Feldman MA, Wisemandle W, Bekker AY. Monitored anaesthesia care with dexmedeto
midine: A prospective, randomized, double-blind, multicenter trial. Anesth Analg. 2010;110(1):47–56.
12. Thota RS, Ambardekar M, Likhate P. Conscious sedation for middle ear surgeries: A comparison between fentanyl-propofol
and fentanyl-midazolam infusion. Saudi J Anaesth [Internet]. 2015;9(2):117–21. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
pubmed/25829896%0Ahttp://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=PMC4374213
13. Benedik Janez MA. Sedation for middle ear surgery: prospective clinical trial comparing propofol and midazolam. Cent Eur J
Med. 2008;3(4):487–93.
14. Gessler EM, Hart AKE, Dunlevy TM, Greinwald JH. Optimal concentration of epinephrine for vasocon striction in ear surgery.
Laryngoscope. 2001;111(10):1687–90.
15. Singh S. Study of tympanomastoidectomy under local anaesthesia using bupivcaine. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.
1995;2(2):144–6.
16. Liang S, Irwin MG. Review of Anaesthesia for Middle Ear Surgery. Anesthesiol Clin [Internet]. 2010;28(3):519–28. Available
from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.anclin.2010.07.009