Abstract
Introduction: Neonatal seizure is the most frequent neurological symptom occurring during the neonatal period. The present study was done to determine the clinical types and the etiological factor of neonatal seizures.
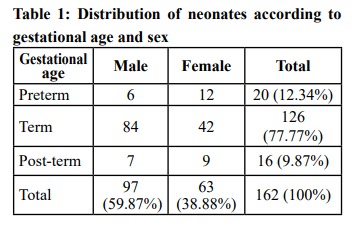
Materials and Methods: This was a prospective, cross-sectional study done at Pokhara Academy of Health Sciences including 162 neonates admitted with a diagnosis of neonatal seizure inside the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit during a period of one year. The neonatal seizure was classified and the possible cause for the seizure was noted in proforma.
Results: The most common type of seizure was a generalized tonic-clonic seizure (38.27%) followed by subtle (35.18%). The common cause of neonatal seizure was hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (50.61%) followed by sepsis (24.69%) and hypocalcemia (5.55%).
Conclusion: Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy was the commonest cause of seizure in neonates followed by infection. Early detection of the risk factors causing perinatal asphyxia can lead to a decrease in the occurrence of neonatal seizures.