Abstract
Introduction: Diabetes Mellitus is a common and
serious global health problem and is associated
with the complications such as cardiovascular
disease, nephropathy, retinopathy and neuropathy,
which can lead to severe mortality and morbidity.
The purpose of this study was to find out the healthrelated quality of life patients with diabetes mellitus.
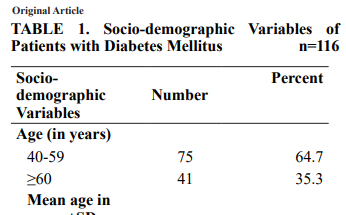
Descriptive cross-sectional research design was
used among 116 patients with diabetes mellitus in
Diabetes, Thyroid and Endocrinology Care Center,
Pokhara via Systematic sampling.
Materials and Methods: Data was collected using
structured World Health Organization Quality of
Life Instrument- Short form: WHOQOL-BREF
tool and analyzed by using computer package with
Statistical Package for Social Science software
version 16. In inferential statistics t- test and
ANOVA test was used to measure the association
between selected demographic variables and overall
HRQOL as well as all the domains at 5 percent level
of significance.
Results: The significant association was observed
between physical, psychological, social and
environment domain with presence of comorbid
illness and complications. The study found that
patients with diabetes mellitus had higher health
related quality of life in environment domain but
lower in social domain. Age below 54 years, male,
duration of disease less than 10 years, living in a
nuclear family and employed respondent had higher
quality of life.
Conclusion: The study concluded the overall
HRQOL is good in patient less than 54 years, male,
married, patient having family history of diabetes,
duration of diabetes less than 10 years, absence of
comorbidity and complications.
References
atlas sixth edition poster update 2014; Available
from: www.idf.org/diabetes-atlas.htm.Retrieved
on April 29, 2018.
2. Visalli N, Cavallo MG, Signore A, Baroni MG,
Buzzetti R, Fioriti E, Mesturino C, Fiori R,
Lucentini L, Matteoli MC, Crinò A. A multi‐
centre randomized trial of two different doses
of nicotinamide in patients with recent‐onset
Type 1 diabetes (the IMDIAB VI). Diabetes/
metabolism research and reviews. 1999
May;15(3):181-5.
3. Mehta RK, Subedi S, Bohora S. Health related
quality of life of diabetic patients visited in
Koshi Zonal Hospital, Biratnanar. Journal of
Chitwan Medical College. 2014;4(3):13-6.
Availablefrom: https://www.nepjol.info/index.
php/JCMC/article/view/11933. Retrieved on
April 29, 2018.
4. Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H.
Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the
year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes
care. 2004 May 1;27(5):1047-53.
5. Gyawali B, Sharma R, Neupane D, Mishra SR,
van Teijlingen E, Kallestrup P. Prevalence of
type 2 diabetes in Nepal: a systematic review
and meta-analysis from 2000 to 2014. Global
health action. 2015 Dec 1;8(1):29088.
6. Silva PA, Soares SM, Santos JF, Silva LB. Cutoff point for WHOQOL-bref as a measure of
quality of life of older adults. Revista de saude
publica. 2014;48:390-7.
7. Sharma S, Joshi S. Health related quality of
life in diabetic patient in selected hospital
Kathmandu. International Journal of Current
Research. 2014; 8(7), 34141-34143. Retrieved
from http:// www.journalcra.com.
8. Mishra S.R, Sharma, A, Bhandari, PM,
Bhochhibhoya S, Thapa K Depression and
health-related quality of life among patients
with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Public Library of
Science. 2015;10(11), 1-13. doi: 10.1371
9. Jain V, Shivkumar S, Gupta O. Health-related
quality of Life (Hr-Qol) in patients with type
2 diabetes mellitus. North American Journal
of Medical Sciences.2014; 6(2), 97-101. doi:
10.4103/1947-2714.127752
10. Kavi A, Walvekar P, Mallapur M. Assessment of
health related quality of life of elderly diabetic
patients attending urban primary health care
facility-a cross sectional study. International
Journal of Community Medicine and Public
Health. 2016 Aug;3(8):2258.
11. Sharma A, Sharma P, Gaur A, Chhabra M, Kaur
R. A cross-sectional study on diabetes mellitus
type-2 at a tertiary care hospital. Adv Res
Gastroentero Hepatol. 2017;8(1):001-6.
12. Kakhki AD. Health-related quality of life
of diabetic patients in Tehran. International
journal of endocrinology and metabolism. 2013
Oct;11(4).
13. Saleh F, Ara F, Mumu SJ, Hafez MA. Assessment
of health-related quality of life of Bangladeshi
patients with type 2 diabetes using the EQ-5D:
a cross-sectional study. BMC research notes.
2015 Dec;8(1):1-8