Abstract
Introduction: To evaluate stone free rate (SFR) with low dose computed tomography-Kidney Ureter Bladder (CT-KUB) after retrograde intrarenal surgery (RIRS) and compare the relation of stone clearance with stone volume and Hounsfield Unit (HU).
Materials and Methods: The prospective observational study was conducted in Bir Hospital from January 2019 to January 2020 . A total of 42 patient with renal stone up to 20 mm size included. Lithotripsy was performed using Holmium laser utilizing High frequency Low Power Energy (HiFrLoPE). Stone clearance was reassessed using low dose CT KUB at 1 month who were stone free on X-ray and ultrasound scan at 2 weeks. Patients were categorized as complete stone free, clinically insignificant Residual Fragment (CIRF) <4 mm and CIRF > 4 mm.
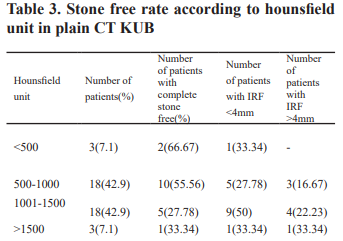
Results: The mean stone volume and HU were 553.37±338.10 and 1063.5±378.07 respectively. Complete SFR was 59% and 35.7% with stone volume <500 and 500-1000 mm3 (P<0.05) respectively. Similarly, Complete SFR was 66.67% and 33.34% with HU<500 and >1500 (P<0.05) respectively. We achieved complete stone clearance in 18 patients (42.85%), whereas 16 patients (38.09%) had CIRF < 4mm and 8 patients (19.04%) had CIRF > 4mm.Low dose CT KUB detected stones in 57.25% patients who were considered stone free based on X-ray and USG KUB findings.
Conclusion: SFR in RIRS is high for renal stones with lower stone volume and low HU. Low dose CT KUB allows more accurate detection of residual fragments than X-ray and USG KUB during follow up of patients after RIRS.
References
Worldwide Trends of Urinary Stone Disease
Treatment Over the Last Two Decades: A Systematic
Review. J Endourol 31 (6):547-556. doi:10.1089/
end.2016.0895
2. Ho CC, Hafidzul J, Praveen S, Goh EH, Bong JJ,
Lee BC, Zulkifli MZ (2010) Retrograde intrarenal
surgery for renal stones smaller than 2 cm. Singapore
Med J 51 (6):512-515
3. Parikh KP, Jain RJ, Kandarp AP (2018) Is
retrograde intrarenal surgery the game changer in
the management of upper tract calculi? A singlecenter single-surgeon experience of 131 cases. Urol
Ann 10 (1):29-34. doi:10.4103/ua.ua_118_17
4. Sheafor DH, Hertzberg BS, Freed KS, Carroll
BA, Keogan MT, Paulson EK, DeLong DM, Nelson
RC (2000) Nonenhanced helical CT and US in the
emergency evaluation of patients with renal colic:
prospective comparison. Radiology 217 (3):792-
797. doi:10.1148/radiology.217.3.r00dc41792
5. Middleton WD, Dodds WJ, Lawson TL, Foley
WD (1988) Renal calculi: sensitivity for detection
with US. Radiology 167 (1):239-244. doi:10.1148/
radiology.167.1.3279456
6. Niemann T, Kollmann T, Bongartz G (2008)
Diagnostic performance of low-dose CT for the
detection of urolithiasis: a meta-analysis. AJR
Am J Roentgenol 191 (2):396-401. doi:10.2214/
7. Türk C, Petřík A, Sarica K, Seitz C, Skolarikos
A, Straub M, Knoll T (2016) EAU Guidelines on
Interventional Treatment for Urolithiasis. Eur Urol
69 (3):475-482. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2015.07.041
8. Muniasamy S PV, Krishnamoorthy S, Kumaresan
N, Ramanan V (2017) Comparative Study of Stone
Free Rate, Morbidity and Need for Retreatment
Procedures between Various Surgical Modalities
for 10-20 mm Upper Urinary Tract Calculi. Int J Sci
Stud 4 (10):37-43. doi:10.17354/ijss/2017/08
9. Lim SH, Jeong BC, Seo SI, Jeon SS, Han DH
(2010) Treatment outcomes of retrograde intrarenal
surgery for renal stones and predictive factors
of stone-free. Korean J Urol 51 (11):777-782.
doi:10.4111/kju.2010.51.11.777
10. Zeng G, Zhang T, Agrawal M, He X, Zhang W,
Xiao K, Li H, Li X, Xu C, Yang S, de la Rosette
JJ, Fan J, Zhu W, Sarica K (2018) Super-mini
percutaneous nephrolithotomy (SMP) vs retrograde
intrarenal surgery for the treatment of 1-2 cm lowerpole renal calculi: an international multicentre
randomised controlled trial. BJU Int 122 (6):1034-
1040. doi:10.1111/bju.14427
11. Hyams ES, Munver R, Bird VG, Uberoi J, Shah
O (2010) Flexible ureterorenoscopy and holmium
laser lithotripsy for the management of renal stone
burdens that measure 2 to 3 cm: a multi-institutional
experience. J Endourol 24 (10):1583-1588.
doi:10.1089/end.2009.0629
12. Zilberman DE, Mor Y, Duvdevani M, Ramon J,
Winkler HZ (2007) Retrograde intra-renal surgery
for stone extraction. Scand J Urol Nephrol 41
(3):204-207. doi:10.1080/00365590601016321
13. Sabnis RB, Ganesamoni R, Doshi A, Ganpule
AP, Jagtap J, Desai MR (2013) Micropercutaneous
nephrolithotomy (microperc) vs retrograde
intrarenal surgery for the management of small
renal calculi: a randomized controlled trial. BJU Int
112 (3):355-361. doi:10.1111/bju.12164