Abstract
Background :
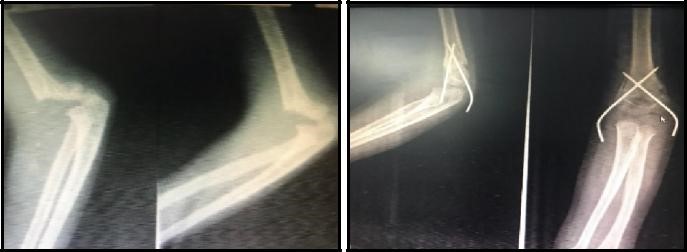
Supracondylar fracture of the distal humerus is one of the commonest fracture in pediatric age group. Though there is consensus of treating type III fracture operatively, no study has compared the outcome between Closed Reduction and Percutaneous Pinning (CRPP) and Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF) with k-wire in our setup.
Materials and Methods:
Retrospective comparison study was done on eighty seven cases of Type III supracondylar fracture of distal humerus underwent operative procedure. Fifty four (54) cases underwent CRPP and 33 cases were managed with ORIF with k-wire, and they were followed up till 6 months post-operatively.
Results :
The mean time for radiological union in patient who underwent CRPP was 4.37±0.94 weeks and that for the patient who underwent ORIF was 4.45±0.13 weeks, the difference of which was statistically insignificant (p-value >0.05). 83.3% of CRPP group and 78.8% in ORIF group had excellent functional outcome and only 3% in ORIF group had poor functional outcome.
Conclusion :
Though both the group don’t have significant advantage of functional outcome among each other CRPP with limited attempt should be preferred to ORIF with k-wire for the advantage of avoiding surgical scar and reducing surgery time and exposure to anaesthetic agents.
References
2. Cheng JC, Shen W. Limb fracture pattern in different pediatric age groups: a study of 3,350 children. Journal of orthopaedic trauma. 1993; 7(1):15-22
3. Gartland JJ. Management of supracondylar fractures of the humer-us in children. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1959
4. Bashyal RK, Chu JY, Schoenecker PL, Dobbs MB, Luhmann SJ, Gordon JE. Complications after pinning of supracondylar distal hu-merus fractures. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics. 2009; 29(7):704-8
5. Camus T, MacLellan B, Cook PC, Leahey JL, Hyndman JC, El-Ha-wary R. Extension type II pediatric supracondylar humerus fractures: a radiographic outcomes study of closed reduction and cast immobili-zation. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics. 2011; 31(4):366-71
6. Kasser J. Percutaneous pinning of supracondylar fractures of the humerus. Instructional course lectures. 1992; 41:385-90
7. Oetgen ME, Mirick GE, Atwater L, Lovejoy JF. Complications and predictors of need for return to the operating room in the treat-ment of supracondylar humerus fractures in children. The open ortho-paedics journal. 2015; 9:139
8. Pretell Mazzini J, Rodriguez Martin J, Andres Esteban EM. Surgi-cal approaches for open reduction and pinning in severely displaced supracondylar humerus fractures in children: a systematic review. Journal of children’s orthopaedics. 2010; 4(2):143-52
9. O’hara L, Barlow J, Clarke NM. Displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. Bone & Joint Journal. 2000; 82(2):204-10
10. Gupta N, Kay RM, Leitch K, Femino JD, Tolo VT, Skaggs DL. Effect of surgical delay on perioperative complications and need for open reduction in supracondylar humerus fractures in children. Jour-nal of Pediatric Orthopaedics. 2004;24(3):245-8
11. Damelsson L, Petterssox H. Open reduction and pin fixation of severely displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in chil-dren. Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica. 1980; 51(1-6):249-55
12. Hart G, Wilson D, Arden G. The operative management of the difficult supracondylar fracture of
the humerus in the child. Injury. 1977;9(1):30-4.
13. Mehlman C, Crawford A, McMillion T, Roy D. Operative treatment of supracondylar fractures of
the humerus in children: the Cincinnati experience. Acta Orthopaedica Belgica. 1996;62:41-50.
14. Furrer M, Mark G, Rüedi T. Management of displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in
children. Injury. 1991;22(4):259-62.
15. Oh C-W, Park B-C, Kim P-T, Park I-H, Kyung H-S, Ihn J-C. Completely displaced supracondylar
humerus fractures in children: results of open reduction versus closed reduction. Journal of orthopaedic
science. 2003;8(2):137-41.
16. Kumar R, Kiran EK, Malhotra R, Bhan S. Surgical management of the severely displaced
supracondylar fracture of the humerus in children. Injury. 2002;33(6):517-22.
17. Mangwani J, Nadarajah R, Paterson J. Supracondylar humeral fractures in children. Bone & Joint
Journal. 2006;88(3):362-5.
18. Shaw BA, Kasser JR, Emans JB, Rand FF. Management of vascular injuries in displaced
supracondylar humerus fractures without arteriography. Journal of orthopaedic trauma. 1990;4(1):25-9.
19. Schoenecker PL, Delgado E, Rotman M, Sicard GA, Capelli AM. Pulseless arm in association with
totally displaced supracondylar fracture. Journal of orthopaedic trauma. 1996;10(6):410-5.